Showing posts with label CIVIL ENGINEERING. Show all posts
Showing posts with label CIVIL ENGINEERING. Show all posts
Bending Stress in Beam Questions - Strength of Material - civil engineering
Bending stress in Beam - Strength of Material
CIVIL ENGINEERING QUESTIONS
Previous year civil engineering questions related to strength of material (SOM) subject topic Bending stress in Beam asked in UPSC ESE examination.
Section Modulus of Important section
 |
| section modulus of rectangular,solid circular, hollow circular and triangular section |
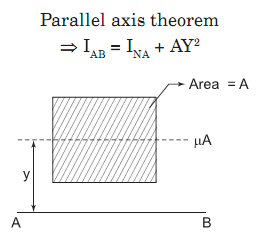
Parallel Axis theorem
Perpendicular Axis theorem
 |
| Perpendicular Axis theorem |
Flexural Formula
Shear stress in beam Questions - Strength of Material civil engineering
Shear stress in Beam - Strength of Material
CIVIL ENGINEERING QUESTIONS
Previous year civil engineering questions related to strength of material (SOM) subject topic shear stress in Beam asked in UPSC ESE examination.
Shear Force per unit length = `H/x` = `(VAy)/I`
Shear stress at the level y from N.A. = q = `(VAy)/Ib`
Shear stress in Rectangular beam
 |
| Shear stress in rectangular beam |
Shear stress in I section
 |
| shear stress in I section |
Shear stress in circular section
 |
Shear stress in triangular section |
Shear stress in Quadrilateral section about diagonal
 |
| Shear stress in Quadrilateral section about diagonal |

Civil Engineering Study with VK
Civil Engineering Study all topics related to this sites
- ▼ July
- List of Surveying Tools and Instruments
- Compass - Surveying tools and Instruments
- Assumptions for the design of Laced columns
- Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering MCQ
- ICMR- National Institute for Research in Tuberculo...
- Composition of Good Brick Earth and its Properties...
- Test for Moisture on soil or Determination of Wate...
- TOTAL POST: 4045 CRP Clerks-XIII for vacancies of ...
- TOTAL POSTS: 257 upsc AE &OTHERS Union Public Serv...
- Friction and Pressure Drag on a body moving throug...
- Rajasthan Public Service Commission (RPSC) Rajasth...
- Find Initial and Final Setting Time of Cement
- Kerala Public Service Commission (KPSC) invites th...
- Chain Survey - Introduction and Condition for its ...
- Temporary Adjustment of SURVEYING Instrument in C...
- Surveyor compass versus Prismatic Compass - Compa...
- Types of Chain and its length for Surveying work i...
- List of Surveying Tools and Instruments
- ▼ June
- Properties of First class brick
- Storage of Cement Bags on Site, How to -
- 15 Different Types of Cement in India and Their Uses
- Slump Cone Test - measures the consistency of fres...
- Sloped Ceiling above Toilet
- 1 Bag of Cement Volume
- How to calculate the volume of sand , aggregate an...
- National Institute of Malaria Research (NIMR) invi...
- Indian Oil Corporation Limited (IOCL) Recruitment ...
- Graduate Engineers - NMDC Limited is a Navaratna P...
- Assistant Engineer-I Damodar Valley Corporation (D...
- Trainee-1 Delhi Pollution Control Committee invite...
- JE IIT Kharagpur - Indian Institution of Kharagpur...
- Bhel-Bharat Electronics Limited a Navartna Company...
- Properties of First class brick
- ▼ April
- The distance between successive vehicles moving in...
- Question-Answer Plate bearing test,highway constru...
- QUESTION-ANSWER - CEMENT CONCRETE PAVEMENTS MAXIMU...
- SAFE STOPPING SIGHT DISTANCE AND ECONOMIC DESIGN O...
- Low-altitude aerial photographs, Length of Curve a...
- In Map versus Aerial photograph, due to symbolic r...
- The levelling is carried out between two stations ...
- A line AB between the stations A and B was measure...
- Which one of the following consists of horizontal ...
- Which one statements is NOT correct - Trigonometri...
- Dip fault is a fault plane parallel to the dip of ...
- Correct statement sub-surface investigation: To es...
- Which one of the following statements is NOT corre...
- Which one of the following is the part of assumpti...
- Which one of the following is a correct general co...
- Which one of the following is an assumption made b...
- By means of Boussinesq’s stress distribution theor...
- The length of a line originally 100 mm long on a m...
- A footing 3m×1.5m in plan transmits a pressure of ...
- Which one of the following coffer dams is suitable...
- The unified classification system is based on the ...
- Consider the following statements related to ultim...
- Which one of the following is an advantage when ge...
- Which one of the following is NOT the common nomen...
- The ultimate bearing capacity is the minimum gross...
- According to Terzaghi, a foundation is shallow if its
- The distance between successive vehicles moving in...
- ▼ March
- INTERPRETATION OF FLOWNET - IN SOIL MECHANICS
- Walls and Its Type - In Civil Engineering Study
- PHASES OF SOIL INVESTIGATION WORK
- Lime - Tests on Limestone
- Lime - Types and Properties of LIme
- Index Properties and Key Parameter of Soil - Civil...
- Common Building Stones - Qualities and Uses
- Stability of Slopes in Earth Dam
- The Economist Nicholas Stern gave the most Impress...
- Canal Falls - Irrigation Engineering
- Docks and Harbour - Civil Engineering study
- Stiffeners - Plate Girder
- Matrix Method of Structure Analysis - Stiffness an...
- INTERPRETATION OF FLOWNET - IN SOIL MECHANICS
- ▼ July
- ▼ 2022
- ▼ January
- Basic Definitions and Simple Tests on Soil Mechanics
- Soil Structure and Clay Mineralogy
- Soil Mechanics - Study all topics
- Qualities of Good Timber - Building Material - Civ...
- Natural Seasoning and Artificial Seasoning of Timber
- Building Materials - All content topic oriented
- Civil Engineering Subjects
- CSEB JE/AE CIVIL QUESTION PAPERS 2018 for CSPHCL R...
- Basic Definitions and Simple Tests on Soil Mechanics
- ▼ January
- ▼ 2021
- ▼ March
- Plasticizer charts - Admixtures used in RCC
- Irrigation - Civil Engineering
- Fluid Mechanics - Important Points before Exam
- Soil Mechanics - Civil Engineering
- Quick revision - Civil engineering
- Civil engineering - QUICK REVISION
- Quick Revision of Civil Engineering - Test-3
- Quick revision of Civil Engineering - Test 2
- QUICK REVISION of Important points before exam - C...
- Transportation Engineering - Civil Engineering
- Reinforced Concrete Construction RCC - Civil Engin...
- Surveying - Most Important topics for Civil Engine...
- Estimation, Costing and Construction Management - ...
- Structural Steel and Metal- Civil Engineering
- Masonry and Tunnel - Related to Brick and Stones
- Strength of Material Civil Engineering
- Paint - Building Material Civil Engineering - Quic...
- Plastics, Glasses and miscellaneous Building Mater...
- Test on building Materials
- Steel Building Material Civil Engineering
- Bitumen Building material - Civil Engineering
- Civil Engineering - Strength of Material- quick re...
- Stone Building Material Civil Engineering
- Cement, Mortar and Concrete - Building Material - ...
- Civil engineering - Building Material - Important ...
- Civil engineering - Building Material - Timber
- Civil engineering - Building Materials - mortar an...
- Civil engineering - Building materials - Bricks Study
- Plasticizer charts - Admixtures used in RCC
- ▼ February
- Building Materials- MCQ on Plastic and tiles
- Building Material- Crushing strength of good stone
- Building Material - self compacted concrete
- Building Material - Hydration of Portland Cement
- Building Material - Bricks question
- Advantages of Seasoning of timber - Building Material
- Concrete, Cement, Timber, Sand, Workabilty and Agg...
- Shear strength of TImber is highest in the direct...
- Building Material
- Building Material
- The impurity of mixing water which affects the set...
- Building Material
- Building material
- Density of high-density Concrete - Building material
- Building material
- Workability of Concrete - Building Materials
- Building material - PAINT - MCQ
- Building Material
- Building Material - PAINT - MCQ
- Building Material - PVCN full form - PAINT
- Building Material
- Building Material
- Building Material
keyword - civil study vk, civil engineering study vk, quick revision of bricks,bricks study vk, cement mortar and concrete
- Building Materials- MCQ on Plastic and tiles
- ▼ March
The distance between successive vehicles moving in the same line measured from head at any instance is-
Question-Answer
The distance between successive vehicles moving in the same line measured from head at any instance is
- (a) the space headway
- (b) the time headway
- (c) the one-way stream
- (d) the head-way stream
(A)
The roads which are provided with a hard pavement course having at least a water bound macadam (WBM) layer are classified as
- (a) Paved roads
- (b) Unpaved roads
- (c) Surface roads
- (d) Unsurfaced roads
(A)
The planning surveys about engineering studies consists of
- (a) Income per capita
- (b) Living standard
- (c) Traffic volume
- (d) Road location and alignment studies
(D)
A cipolletti weir has length of 2.0 m and head over the weir is 1 m. What is the discharge over the weir? (Take Cd = 0.62)
- (a) 10.35 m3/s
- (b) 3.66 m3/s
- (c) 45.21 m3/s
- (d) 75.68 m3/s
(B)
Q = 2 /3 Cd (2g)1/2 H3\2
Q = 2 /3 Cd (2g)1/2 H3\2
Which one of the following is an advantage using a triangular notch over a rectangular notch?
- (a) Ventilation of a triangular notch is necessary
- (b) The same triangular notch cannot measure a wide range of
flows accurately
- (c) For heavy discharges, a triangular notch gives more accurate
results than a rectangular
notch.
- (d) In a given triangular notch, only one reading is required to be taken for the measurement of discharge
(D)
A triangular notch is preferred to a rectangular notch due to following reasons:
1. The expression for discharge for a right angled V-notch is very simple.
2. For measuring low discharge, a triangular notch gives more accurate results than
a rectangular notch.
3. In case of triangular notch, only one reading, i.e., H is required for the computation
of discharge.
4. Ventilation of triangular notch is not necessary.
A triangular notch is preferred to a rectangular notch due to following reasons:
1. The expression for discharge for a right angled V-notch is very simple.
2. For measuring low discharge, a triangular notch gives more accurate results than
a rectangular notch.
3. In case of triangular notch, only one reading, i.e., H is required for the computation
of discharge.
4. Ventilation of triangular notch is not necessary.
 |
| Question-Answer civil engineering study |
Question-Answer Plate bearing test,highway constructionwork,and cant
Which one of the following tests is carried out using a relatively large diameter plate to evaluate the load supporting capacity of pavement layers?
- (a) California bearing ratio test
- (b)California resistance value test
- (c) Triaxial compression test
- (d) Plate bearing test
(D)
Consider the following aspects of human vision which are important for
a traffic engineer:
1. Field of vision
2. Visual acuity
3. Colour perception
Which of the above aspects are correct?
- (a) 1 and 2 only
- (b) 2 and 3 only
- (c) 1 and 3 only
- (d) 1, 2 and 3
(D)
The survey of the highway construction work for preparation of longitudinal and cross sections, computations of earth work quantities; and other construction material and checking details of geometric design elements is carried out in
- (a) Reconnaissance survey
- (b) Preliminary survey
- (c) Location of final alignment
- (d) Detailed survey
(B)
The raising of outer rail over inner rail is called
- (a) Cant deficiency
- (b) Cant
- (c) Capacity of the track
- (d) Center bound sleepers
(B)
Super elevation or cant –
Outer rail raised with respect to inner rail in order to generate centripetal force against
centrifugal force which occurs outward in horizontal plane from CG of vehicle.
Super elevation or cant –
Outer rail raised with respect to inner rail in order to generate centripetal force against
centrifugal force which occurs outward in horizontal plane from CG of vehicle.
 |
| Question-Answer civil engineering study |
QUESTION-ANSWER - CEMENT CONCRETE PAVEMENTS MAXIMUM UTILITY PER UNIT LENGTH AND TUNNELING
Question-Answer
The longitudinal joints in cement concrete pavements are constructed with suitable
- (a) tie bars
- (b) torsion rods
- (c) small spacing
- (d) shear rods
(A)
In which one of the following systems the optimum road length is calculated for an area based on the concept of obtaining maximum utility per unit length of road?
- (a) Saturation system
- (b) Unsaturated system
- (c) Minimum utility system
- (d) Average utility system
(A)
Which one of the following alignments is obtained by development accompanied by tunneling?
- (a) Valley alignment
- (b) Cross country alignment
- (c) Mountain alignment
- (d) Zig-zag alignment
(C)
The alignment of a tunnel constructed as part of a development project would depend
on various factors, such as the topography of the area, the geological conditions, and
the tunnel's purpose. A zig-zag alignment would not typically be used in tunnel
construction, as it would increase construction costs and complexity without providing
significant benefits. A "Mountain Alignment" typically refers to a tunnel alignment that
follows the contour of a mountain or hill. This type of alignment is often used when a
tunnel is needed to bypass a mountainous area or provide access to resources within
a mountain. However, it is important to note that the alignment chosen for a tunneling
project would depend on a wide range of factors, such as the area's geology, the
presence of other infrastructure, and the project's specific needs.
 |
| Question-Answer civil engineering study |
SAFE STOPPING SIGHT DISTANCE AND ECONOMIC DESIGN OF MODERN TRACK
Question-Answer
The design speed for a two-way traffic on a two way lane road is 50 kmph. What is the value of safe stopping sight distance, if co-efficient of friction is 0.37 and reaction time of driver as 2.5 sec?
- (a) 34.8 m
- (b) 61.4 m
- c) 122.8 m
- (d) 193.5 m
(B) 61.4 m
SSD = 0.278V.t + V2/254f
SSD = 0.278 × 50 × 2.5 × 502/(254 × .37)
SSD = 61.4m
SSD = 0.278V.t + V2/254f
SSD = 0.278 × 50 × 2.5 × 502/(254 × .37)
SSD = 61.4m
Consider the following statements related to economic design of
modern track:
1. Axle loading, possible
weight reduction of the rolling stock and increase in number
of axles should be rationalized.
2. Rail to sleeper
fastenings for different type of sleepers at high speeds should have
definite standards.
3. The weight of the sleeper and the rail may not be related to each other. Which of the above statements are correct?
- (a) 1 and 2 only
- (b) 2 and 3 only
- (c) 1 and 3 only
- (d) 1, 2 and 3
(A)
A modern track has to be rationalized in view of the following to achieve over-all economy on Indian Railways.
A modern track has to be rationalized in view of the following to achieve over-all economy on Indian Railways.
- i. Rail requirements, like quality of steel, design of rail-section and manufacturing
process, should be rationalized so that the rail section can sustain the expected
stresses due to rolling loads.
- ii. Wheel diameter in relation to qualities of rail steel and steel of the wheel tyre should
also be rationalized so as to keep Hertzian stresses within the endurance limits of
the steel.
- iii. Axle loading, possible weight reduction of the rolling stock and increase in number of axles should be rationalized. iv. Rail-to-sleeper fastenings i.e., elastic fastenings for different types of sleepers at high speeds should have definite standards. v. The weight of the sleeper and the rail should be correctly related to each other
 |
| Question-Answer civil engineering study |
Low-altitude aerial photographs, Length of Curve and Long cord
In multilevel classification system, Level IV classification is suitable for
- (a) Landsat MSS images
- (b) High-altitude aerial photographs
- (c) Low-altitude aerial photographs
- (d) Medium-altitude aerial photographs
(C) LOW-ALTITUDE AERIAL
PHOTOGRAPH
| LEVEL |
SYSTEM |
IMAGE SCALE |
| I |
Landsat TM and MSS images; AVHRR
images |
Smaller than 1:250,000 |
| II |
High-altitude aerial
photographs; TM and SPOT images AVHRR images (with ancilliary data) |
1:80,000 to 1:250, 000 |
| III |
Medium-altitude aerial
photographs |
1:20,000 to 1:80, 000 |
| IV |
Low-altitude aerial photographs |
Larger than 1:20,000 |
Directions for the following (02) items:
Read the following information and
answer the two items that follow:The chainage of the intersection point
of two straights is 1060 m, and the angle of intersection is
120°. If radius of a circular curve to be set out is 570 m, and
peg interval Is 30 m.
What is the length of the curve?
- (a) 190π m
- (b) 185π m
- (c) 180π m
- (d) 170π m
(A) 190π m
Length of curve = Angle subtended at O × Radius
L = π/3 × 570 = = 190π m
Length of curve = Angle subtended at O × Radius
L = π/3 × 570 = = 190π m
What is the length of the long chord?
- (a) 370 m
- (b) 470 m
- (c) 670 m
- (d) 570 m
(D) 570 m
Length of long chord = AB =2Rsin (∆/2) = 2Rsin (60/2) =2Rsin (30)
2×R×1/2 = 2×570×1/2= 570m
Length of long chord = AB =2Rsin (∆/2) = 2Rsin (60/2) =2Rsin (30)
2×R×1/2 = 2×570×1/2= 570m
 |
| Question-Answer civil engineering study |
In Map versus Aerial photograph, due to symbolic representation the clarity of details is -
Question-Answer:
In Map versus Aerial photograph, due to symbolic representation the clarity of details is
- (a) less on map than on a photo
- (b) more on map than on a photo
- (c) less on a photo than on map
- (d) more on a photo than on map
Ans. (b)
Differences between Map and Aerial
Photograph,
1. The map is an orthographic projection, whereas an aerial photograph is a central projection, i.e. perspective projection.
2. The map has a single constant scale, whereas it varies from point to point depending upon their elevations in an aerial photograph. In the case of the photograph, the terrain area which has higher elevation is closer to the camera and therefore appears larger than the terrains area laying at a lower elevation.
3. The number of details on a map are selective whereas in a aerial photograph there is a large number of details.
4. Due to the symbolic representation, the clarity of details is more on the maps than on photo.
1. The map is an orthographic projection, whereas an aerial photograph is a central projection, i.e. perspective projection.
2. The map has a single constant scale, whereas it varies from point to point depending upon their elevations in an aerial photograph. In the case of the photograph, the terrain area which has higher elevation is closer to the camera and therefore appears larger than the terrains area laying at a lower elevation.
3. The number of details on a map are selective whereas in a aerial photograph there is a large number of details.
4. Due to the symbolic representation, the clarity of details is more on the maps than on photo.
next
 |
| Question-Answer civil engineering study |
Other Important Topic Related to Surveying in Civil engineering
The levelling is carried out between two stations P and Q separated by 1000 m. The Back Sight (BS) reading is noted as 0.70 m on station P, whose BM is 240.00 m. Next, the Fore Sight (FS) reading is taken on an intermediate point and the value is 1.25 m. Then the instrument is shifted to a new location and BS is taken on intermediate point as 0.85 m. Finally, the FS reading is taken on station Q as 1.10 m. What is the Reduced Level of Q?
Question-Answer:
The levelling is carried out between two
stations P and Q separated by 1000 m. The
Back Sight (BS) reading is noted as 0.70 m on station P, whose BM is
240.00 m. Next,
the Fore Sight (FS) reading is taken on an intermediate point and the
value is 1.25 m.
Then the instrument is shifted to a new location and BS is taken on
intermediate point
as 0.85 m. Finally, the FS reading is taken on station Q as 1.10 m.
What is the Reduced
Level of Q?
- (a) 239.20 m
- (b) 240.80 m
- (c) 241.25 m
- (d) 241.80 m
Ans. (a)
so R.L. of Q
239.20m
| POINTS |
BS |
FS |
HI |
RL |
| P |
.7 |
240.7 |
240 |
|
| INTERMEDIATE |
.85 |
1.25 |
240.3 |
239.45 |
| Q |
1.1 |
239.2 |
239.20m
next
 |
| Question-Answer civil engineering study |