Shear stress in Beam - Strength of Material
CIVIL ENGINEERING QUESTIONS
 |
Question-Answer civil engineering study
|
Previous year civil engineering questions related to strength of material (SOM) subject topic shear stress in Beam asked in UPSC ESE examination.
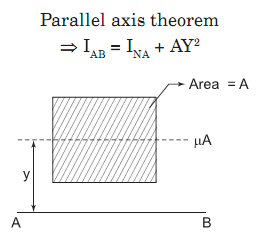
Shear Force per unit length = `H/x` = `(VAy)/I`
Shear stress at the level y from N.A. = q = `(VAy)/Ib`
Shear stress in Rectangular beam
 |
| Shear stress in rectangular beam |
Shear stress in I section
 |
| shear stress in I section |
Shear stress in circular section
 |
| shear stress in circular section |
Shear stress in triangular section
 |
Shear stress in triangular section |
Shear stress in Quadrilateral section about diagonal
 |
| Shear stress in Quadrilateral section about diagonal |