Ultimate bearing capacity: It is the minimum pressure at the base of the foundation soil fails in shear.
Safe bearing capacity: It is the maximum pressure at which soil can carry without shear failure.
Net load intensity: It is the minimum net load at which shear failure of soil can occur.
Allowable bearing capacity: The net intensity of loading which the foundation will carry without undergoing settlement in excess or the permissible value for the structure under consideration but not exceeding net safe bearing capacity is termed as allowable bearing capacity.
Sheet Piles:
Sheet piles are similar to retaining walls which are constructed to retain earth, water or any other filling materials. These walls are thinner in section compared to masonry walls.
Sheet pile walls are generally used for water front structures, i.e. in building wharfs, quays and piers, building diversion dams, such as cofferdams, river bank protection and retaining the sides of cuts made in earth.
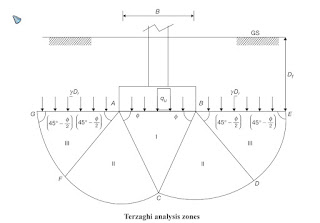
Based on the Assumptions,
Terzaghi Theory is applicable for shallow foundation because side shear resistance and stressing of soil above the foundation is ignored whereas,
Meyerhoff considered stress zone extended up to G.L. Hence Meyershoff's theory is applicable for deep footing also.
Type of Footing and Soil | Settlement and contact pressure |
Rigid footing and sand | Settlement : Uniform Contact Pressure: Zero at edges and maximum at center |
Rigid footing and Clay | Settlement : Uniform Contact Pressure: maximum at edges and minimum at center. |
Flexible footing and sand | Settlement: Maximum at edges and minimum at center. Contact Pressure: Uniform |
Flexible footing and Clay | Settlement : Minimum at edges and maximum at center Contact Pressure: Uniform
|
Pile Group
Settlement of a pile group is more than the settlement of a single pile, even when the load is the same. This is because the pressure bulb of the pile group is deeper than that of individual piles, causing the compression of a larger volume of soil by the pile group.
Important Points:
- Pile group settlement for clayey soil can be computed from the principle of consolidation.
- Pile group settlement for sandy soil can be computed from the formula below:
- By Meyerhof’s Formula for square pile group only
- Where
- Sg = group settlement of pile
- Si = individual pile settlement
- B = Width of pile group
- r = number of rows in a pile group
The ultimate bearing capacity of a pile
- The ultimate bearing capacity of a pile is the maximum load which it can carry without failure or excessive settlement of the ground. The bearing capacity also depends upon the method of installation.
- In Analytical method,
- Qup = Qeb + Qsf
- Qup = qb × Ab + qs × As
- Where,
- Qup = ultimate load on pile
- Qeb = end bearing capacity
- Qsf = skin friction
- qb = End bearing resistance of unit area, Ab = bearing Area
- qs = skin friction resistance of unit area, As = surface Area
- For circular footing, ultimate bearing capacity
- qu = 1.3 CNc + γDfNq + 0.3 γBNγ
- For square footing, ultimate bearing capacity
- qu = 1.3 CNc + γDfNq + 0.4 γBNγ
For clay soil- Qup = Nc × C × Ab + α c̅ As;
- qb = Nc × C, qs = α c
- Where, α = adhesion factor
- c̅ = Average cohesion over depth of pile
‘Negative skin friction
- ‘Negative skin friction’ or ‘downward drag’ is a phenomenon which occurs when a soil layer surrounding a portion of the pile settles more than the pile. Such relative motion may occur when the clay stratum undergoes consolidation due to
- 1. A fill recently placed over the clay stratum.
- 2. Lowering of the ground water table.
- 3. Reconsolidation occurring due to disturbance caused by pile driving in sensitive clay stratum, etc.
- The axial capacity of a pile is a summation of upward reaction due to bearing at the base and net upward skin frictional resistance. As the negative skin friction (acting downward) lowers the net skin resistance, it in turn reduces the axial capacity of piles.
- Negative skin friction increases gradually as the consolidation of the clay layer proceeds since the effective overburden pressure gradually increases due to dissipation of excess pore pressure.
According to IS 2911 : Part III 1973, the ratio of bearing resistance for double under- reamed pile to that of single under-reamed pile is 1.5 for sandy and clayey soils including black cotton soils.
Note:-
As per IS 2911: Part III (Some other recommendations)
- 1. For deep deposits of expansive soils the minimum length of piles, irrespective of any other considerations shall be 3.5 m below the ground level. For recently filled up grounds or other strata or poor bearing, the piles should pass through them and rest in good bearing strata.
- 2. The diameter of under-reamed piles may vary from 2 to 3 times the stem diameter depending upon the feasibility of construction. For Bored cast in situ under-reamed piles the bulb diameter normally be 2.5 times while for compaction piles it is 2 times.
- 3. For piles up to 30 cm diameter, spacing of bulbs should not be greater than 1.5 times the diameter of bulb. For piles of diameter greater than 30 cm, spacing can be reduced to 1.25 times the stem diameter.
- 4. The top most bulb should be at a minimum depth of 2 times the bulb diameter. In expansive soils, it should not be less than 1.75 m below ground level. The minimum clearance below underside of pile cap embedded in ground and the bulb should be a minimum 1.5 times the bulb diameter.
- 5. Under reamed piles with more than two bulbs are not advisable without ensuring their feasibility in strata needing stabilisation of boreholes by drilling mud. The number of bulbs in case of bored compaction piles should not exceed tow in such strata.
Retaining Wall
- Retaining wall is a structure that are designed and constructed to withstand lateral pressure of soil or hold back soil materials.
- The lateral pressure could be also due to earth filling, liquid pressure, sand, and other granular materials behind the retaining wall structure.
The empirical formula for determining the depth (d) of retaining wall is given by:
Where, ka is the active earth pressure coefficient and it is given by:
News Record formula is used to determine the ultimate load carrying capacity (Qup) of a pile embedded in sand. It is given by:
Qap=WhFOS(S+C) {For Drop hammer and Single acting steam hammer}
Qap=(W+ap)hFOS(S+C) {For Double acting steam hammer}
Where,
W = Weight if hammer in KN
FOS is Factor of safety which is generally taken ‘6’ for all type of hammers.
H = Height of fall in cm.
S = penetration of pile per blow in cm.
C = Constant for accounting elastic compression of pile and pile cap.
A = area of piston in m2 and p is steam pressure in kN/m2.
The values of S, C and FOS for different type of hammers are given below in tabulated form:
Single acting Hammer | Double acting Hammer | Drop Hammer |
S = Average value for last 25 blows | S = Average value for last 25 blows | S = Average value for last 5 blows |
C = 0.25 cm | No defined value but generally taken C = 0.25 cm. | C = 2.5 cm |
FOS = 6 | FOS = 6 | FOS = 6
|
Local shear failure:
This type of failure is seen in relatively loose sand and soft clay.
Some characteristics of local shear failure are:
- 1. Failure is not sudden and there is no tilting of footing.
- 2. Failure surface does not reach the ground surface and slight bulging of soil around the footing is observed
- 3. Failure surface is not well defined
- 4. Failure is progressive
- 5. In load-settlement curve, there is no well-defined peak
- 6. Failure is characterized by considerable settlement directly beneath the foundation
- 7. A significant compression of soil below the footing and partial development of plastic equilibrium is observed.
- 8. Well-defined wedge and slip surfaces only beneath the foundation.
Load-settlement curve:-
Note: In general shear failure, failure plane circular for cohesive soils and log spiral for sand and silts.
Types of shear failure:
General shear failure:
- It occurs in shallow foundations when placed on dense/stiff soil.
- At the time of failure, the foundation will get tilted and heaving will occur at the side.
- Before failure settlement will be small and negligible and the stress zone extends up to ground level.
Local shear failure:
- It occurs in loose sand and soft clays in case of shallow foundation.
- Before failure large settlement is recorded.
- The stress zone does not extend up to the ground level hence there may e little or no heaving at the sides.
Punching shear failure:
- It occurs in deep footing and pile which are placed on loose sand or soft clays.
- In this failure soil below the foundation gets cut off from adjacent soil by shearing and large settlement is recorded in the small-time period.
- The adjacent soil mass remains unstressed.
Foundtion Condition and Types of Failure
| Foundation condition | Types of shear failure |
| Footings on the surface or at shallow depths in very dense sand | General shear failure |
| Footing on saturated and normally consolidated clay under undrained loading | General shear failure |
| Footings at deeper depth in dense sand | Punching shear failure |
| Footing on the surface or at shallow depths in loose sand | Punching shear failure |
| Footing on very dense sand loaded by transient dynamic load | Punching shear failure |
| Footings on very dense sand underlain by loose sand or soft clay | Punching shear failure |
| Footing on saturated and normally consolidated clay under drained loading | Punching/Local shear failure
|
Different IS codes and their use:
IS 456:2000 - Plain and reinforced concrete
IS 1080: 1985 - Design and construction of shallow foundation in soil (other than a raft, ring, and shell)
IS 1904:1986 - Design and construction of foundations in soils: General requirements
IS 2950: 1981 - Design and construction of raft foundation
IS code specification for permissible settlement:
(i) Total Permissible settlement:
- For isolated footing on clay = 65 mm
- For isolated footing on sand = 40 mm
- For raft footing on clay = 65-100 mm
- For raft footing on sand = 40-65 mm
(ii) Permissible Differential settlement:
- For isolated footing on clay = 40 mm
- For isolated footing on sand = 25 mm
(iii) Permissible angular settlement:
- For high framed structure < 1/500
- To prevent all type of minor damage < 1/1000
Note:
For multi-storeyed buildings having isolated foundations on sand, the maximum permissible settlement is 60 mm
[ For multistorey buildings having isolated foundations take the higher load as compare to single storey buildings having isolated foundations. So that deflection caused by multistorey building having isolated foundation higher than 40 mm (from the safer side)]
Foundtion and their Suitability
The different types of foundations and there suitability is specified in below in tabulated form:
Type of Foundation | Suitability |
Spread footing foundation | This type of foundation can normally be used for three to four-storied buildings on common type of alluvial soils. |
Stepped Foundation. | This type of foundation is provided on hilly places or in those situations where the ground is sloppy. |
Pile Foundations | It is used in the following situations: - When it is not economical to provide spread foundations and hard soil is at a greater depth.
- When it is very expensive to provide raft or grillage foundations.
- When heavy concentrated loads are to be taken up by the foundations.
- When the top soil is of compressible nature.
- When there is chances construction of irrigation canals in the near by area.
- In case of bridges when the scouring is more in the river bed.
- In marshy places.
|
Raft Foundations | This type of foundation is also recommended in such situations where the bearing capacity of the soil is very poor, the load of the structure is distributed over the whole floor area, or where a structure is subjected to constant shocks or jerks. |
Well Foundations | This is generally provided for construction of bridge piers and the foundations are to be carried out in deep sandy soils of soft soils. |